Voraussetzungen: Cygwin (32-Bit Installer oder 64-Bit Installer) , OpenSSH Client (z.b. Putty, Kitty etc.)
Getestet mit: Windows 7 (64-Bit) Server, Windows 7 (32-Bit) Client
Dieser Artikel ist eine Ergänzung zu diesem Artikel
 Für Windows gibt es (fast) keine kostenfreien und zugleich kommerziell einsetzbaren SSH Server mehr. Da diese SSH Pakete meist sowieso auf Cygwin setzen, kann man dies auch gleich installieren (installiert ~ 150 MB) und dann SSH entsprechend konfigurieren.
Für Windows gibt es (fast) keine kostenfreien und zugleich kommerziell einsetzbaren SSH Server mehr. Da diese SSH Pakete meist sowieso auf Cygwin setzen, kann man dies auch gleich installieren (installiert ~ 150 MB) und dann SSH entsprechend konfigurieren.
Was soll das Ganze? -> siehe hier
Geänderte Installation & Konfiguration am Server:
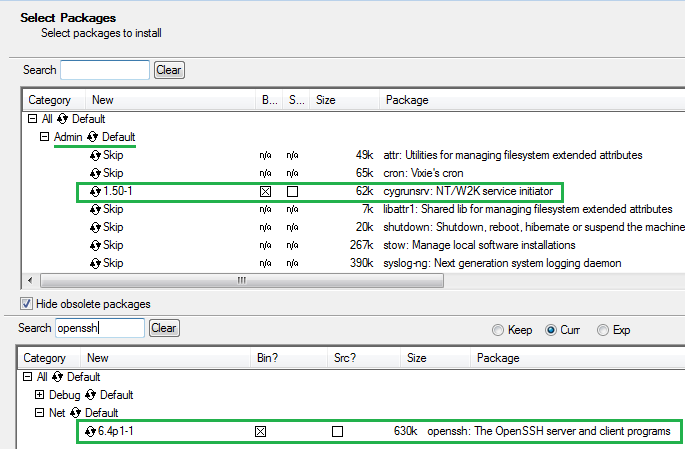
1. Cygwin downloaden und installieren.
2. Cygwin Terminal starten und mit diesem Kommando konfigurieren.
ssh-host-config -y
 Während des Installation wird das Servicekonto “cyg_server” angelegt, dazu muss auch ein Passwort vergeben werden.
Während des Installation wird das Servicekonto “cyg_server” angelegt, dazu muss auch ein Passwort vergeben werden.
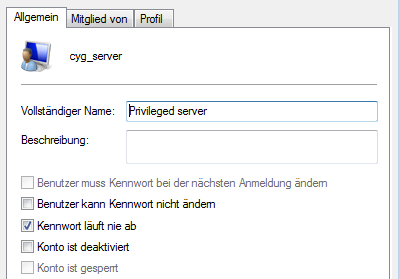 SSH Server starten und beim Neustarten des Systems automatisch mitstarten.
SSH Server starten und beim Neustarten des Systems automatisch mitstarten.
cygrunsrv -S sshd
Jetzt kann man sich mit seinem aktuell angemeldeten (Windows) Benutzernamen / Passwort anmelden und wie im anderen Artikel beschrieben entsprechend Dienste “durchschleifen”.
SSH Server Updates: Empfehlenswert ist außerdem eine Paketverwaltung einzusetzen, wie man sie unter Debian kennt. cyg-apt ist hier das richtige Paket. Damit bleibt dann auch SSH immer auf den neuesten Stand.
Bsp. letztes Sicherheitsproblem (November 2013 vor Openssh 6.4):
OpenSSH Security Advisory: gcmrekey.adv
This document may be found at: http://www.openssh.com/txt/gcmrekey.adv
1. Vulnerability
A memory corruption vulnerability exists in the post-
authentication sshd process when an AES-GCM cipher
(aes128-gcm@openssh.com or aes256-gcm@openssh.com) is
selected during kex exchange.
If exploited, this vulnerability might permit code execution
with the privileges of the authenticated user and may
therefore allow bypassing restricted shell/command
configurations.
2. Affected configurations
OpenSSH 6.2 and OpenSSH 6.3 when built against an OpenSSL
that supports AES-GCM.
3. Mitigation
Disable AES-GCM in the server configuration. The following
sshd_config option will disable AES-GCM while leaving other
ciphers active:
Ciphers aes128-ctr,aes192-ctr,aes256-ctr,aes128-cbc,3des-cbc,blowfish-cbc,cast128-cbc,aes192-cbc,aes256-cbc
4. Details
When using AES-GCM, sshd was not initialising a Message
Authentication Code (MAC) context that is unused when the
cipher mode offers authentication itself. This context
contains some callback pointers, including a cleanup callback
that was still being invoked during a rekeying operation.
As such, the address being called was derived from previous
heap contents.
This vulnerability is mitigated by the difficulty of
pre-loading the heap with a useful callback address and by
any platform address-space layout randomisation applied to
sshd and the shared libraries it depends upon.
5. Credit
This issue was identified by Markus Friedl (an OpenSSH
developer) on November 7th, 2013.
6. Fix
OpenSSH 6.4 contains a fix for this vulnerability. Users who
prefer to continue to use OpenSSH 6.2 or 6.3 may apply this
patch:
Index: monitor_wrap.c =================================================================== RCS file: /cvs/src/usr.bin/ssh/monitor_wrap.c,v retrieving revision 1.76 diff -u -p -u -r1.76 monitor_wrap.c --- monitor_wrap.c 17 May 2013 00:13:13 -0000 1.76 +++ monitor_wrap.c 6 Nov 2013 16:31:26 -0000 @@ -469,7 +469,7 @@ mm_newkeys_from_blob(u_char *blob, int b buffer_init(&b); buffer_append(&b, blob, blen); - newkey = xmalloc(sizeof(*newkey)); + newkey = xcalloc(1, sizeof(*newkey)); enc = &newkey->enc; mac = &newkey->mac; comp = &newkey->comp;
One reply on “RDP/VNC über SSH tunneln (Windows)”
[…] —Update: 24.11.13— Dieser Artikel ist teilweise veraltet, eine neue Version befindet sich hier […]